National Health Profile 2018
Immunization:
India has attained significant progress in achieving immunization coverage through Universal
Immunization Programme (UIP) which provides prevention against six vaccine preventable diseases. In 2013, India
along with South East Asia Region, declared commitment towards measles elimination and rubella/ congenital
rubella syndrome (CRS) control by 2020. MR vaccine campaign is targeted towards 410 million children across the
country
7
. Mission Indradhanush aimed to fully immunize more than 90% of newborns by 2020 through innovative
and planned approaches. A total of 528 districts were covered during the various phases of Mission Indradhanush
8
.
India has come a long way in immunisation but has to traverse far before achieving its targets.
National health programmes
, launched by the Government of India, have been playing crucial roles in tackling
several serious health concerns, communicable and non-communicable diseases, over the last two decades.
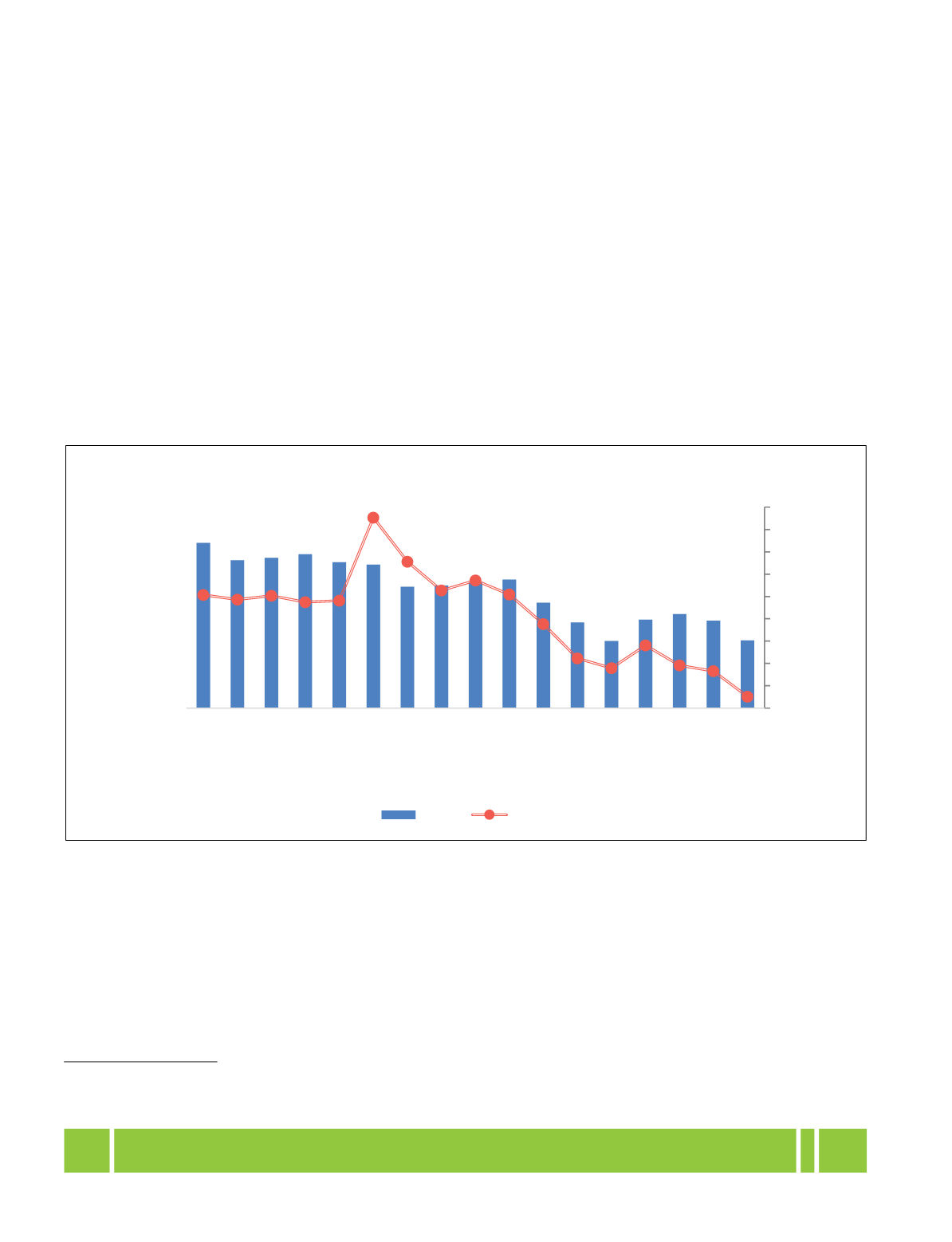
Malaria has been a problem in India for centuries, at one time a rural disease, diversified under the pressure of
developments into various ecotypes. Both the cases reported and deaths due to malaria have come down over the
years. The malarial death rate in India declined to 0.01 deaths per lakh population in 2016 from 0.10 deaths per
lakh population in 2001. To achieve malaria-free country by 2027 and elimination by 2030, National Strategic Plan
(NSP) 2017-22 for Malaria Elimination has been developed by National Vector Borne Disease Control Programme.
For effective implementation of various elimination strategies, the focus of the programme is laid on district-level
rather than State-level.
Female Literacy
IMR
MMR
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
1400
1600
1800
0
500000
1000000
1500000
2000000
2500000
2001
2002
2003
2004
2005
2006
2007
2008
2009
2010
2011
2012
2013
2014
2015
2016
2017
Deaths
Cases
Year
Cases and Deaths due to Malaria in India
Cases
Deaths
Revised National TB Control Programme (RNTCP) is another programme implemented under National Health
Mission. It has achieved millennium development goals in 2015 by halting and reversing the incidence of TB.
The programme was initiated with the objective of ensuring access to quality diagnosis and care for all TB
patients. Several notable activities such as notification of TB; case-based, web-based recording and reporting
system (NIKSHAY); standards of TB care in India; Composite indicator for monitoring programme performance;
scaling up of the programmatic management of drug resistant TB services etc. were implemented in the past.
NIKSHAY, the web based reporting for TB programme has enabled to capture and transfer of individual patient
data from the remotest health centres of the country. In 2017, National Strategic Plan (NSP) 2017-25 for TB
Elimination framework has been adopted, which provides goals and strategies for eliminating TB in India by 2030.
XIV
7 National operational guidelines for introduction of measles –rubella vaccine 2017
8
http://www.missionindradhanush.in/about.html